Kenya
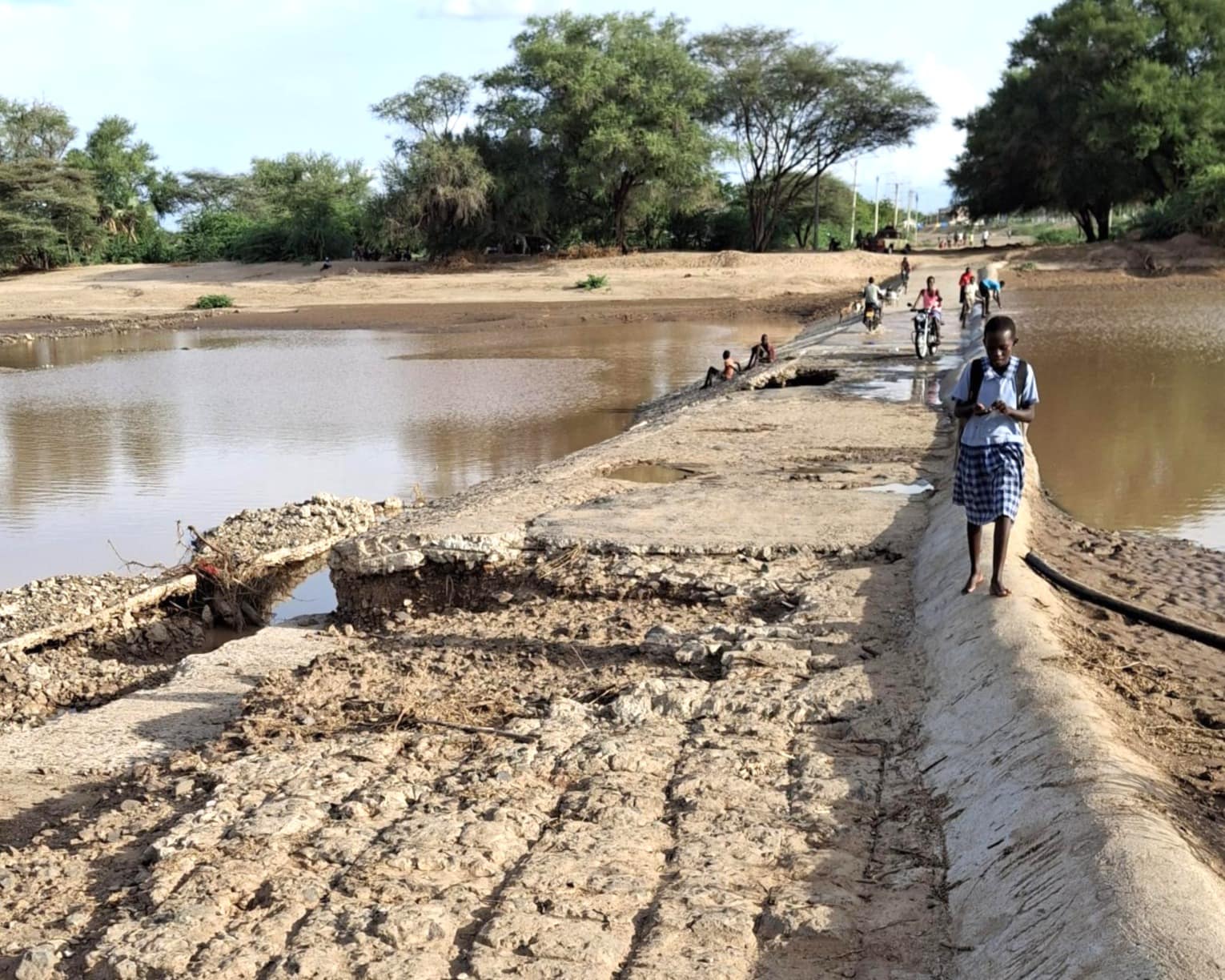
Kenya has a varied climate, with arid and semi-arid areas in the north and east, while the central and western regions experience more temperate conditions due to higher altitudes.
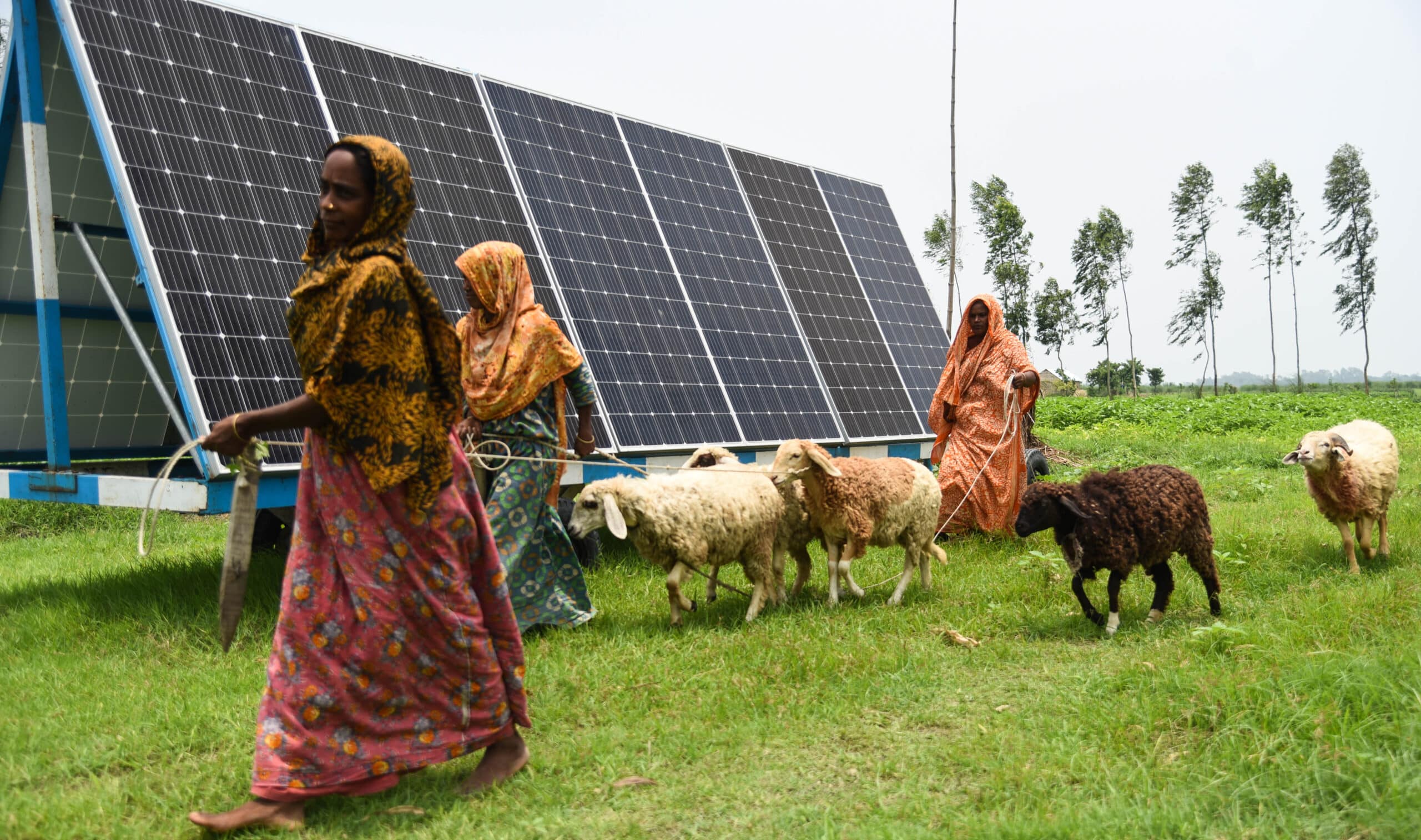
Agriculture plays a vital role in Kenya’s economy, contributing about 33% to its GDP and providing employment for over 75% of the rural population. The sector faces challenges such as fluctuating rainfall patterns, frequent droughts, and soil degradation, which significantly affect smallholder farmers who are key to the country’s agricultural output. Despite these challenges, Kenya is a leader in agricultural innovation in the region, with a growing agritech ecosystem that aims to boost productivity, improve resilience, and create sustainable farming practices.
IWMI in Kenya
IWMI’s work in Kenya focuses on empowering smallholder farmers through the adoption of localized, science-based agritech innovations. Through Agritech4Kenya, IWMI supports the development and scaling of agritech solutions that are tailored to the specific needs of Kenyan farmers, helping to improve productivity and adapt to changing climate conditions. Additionally, IWMI explores the legitimacy of inclusive innovation processes, particularly through the perspectives of smallholder farmers in Uasin Gishu, ensuring that innovations are designed with their input and benefit in mind. By combining technology, knowledge-sharing, and community engagement, IWMI aims to create a more resilient and sustainable agricultural landscape in Kenya.